高能⚠️
(如果您没有听过或不是要寻找快速傅立叶变换Fast Fourier transform(FTT)/离散傅里叶变换Discrete Fourier Transform(DFT)相关的问题,请直接无视这篇文章)
遇到一个通讯专业-波形频谱信号?分析的项目,需要把一组数据做快速傅立叶变换(FTT)后,画出图形(如下图)
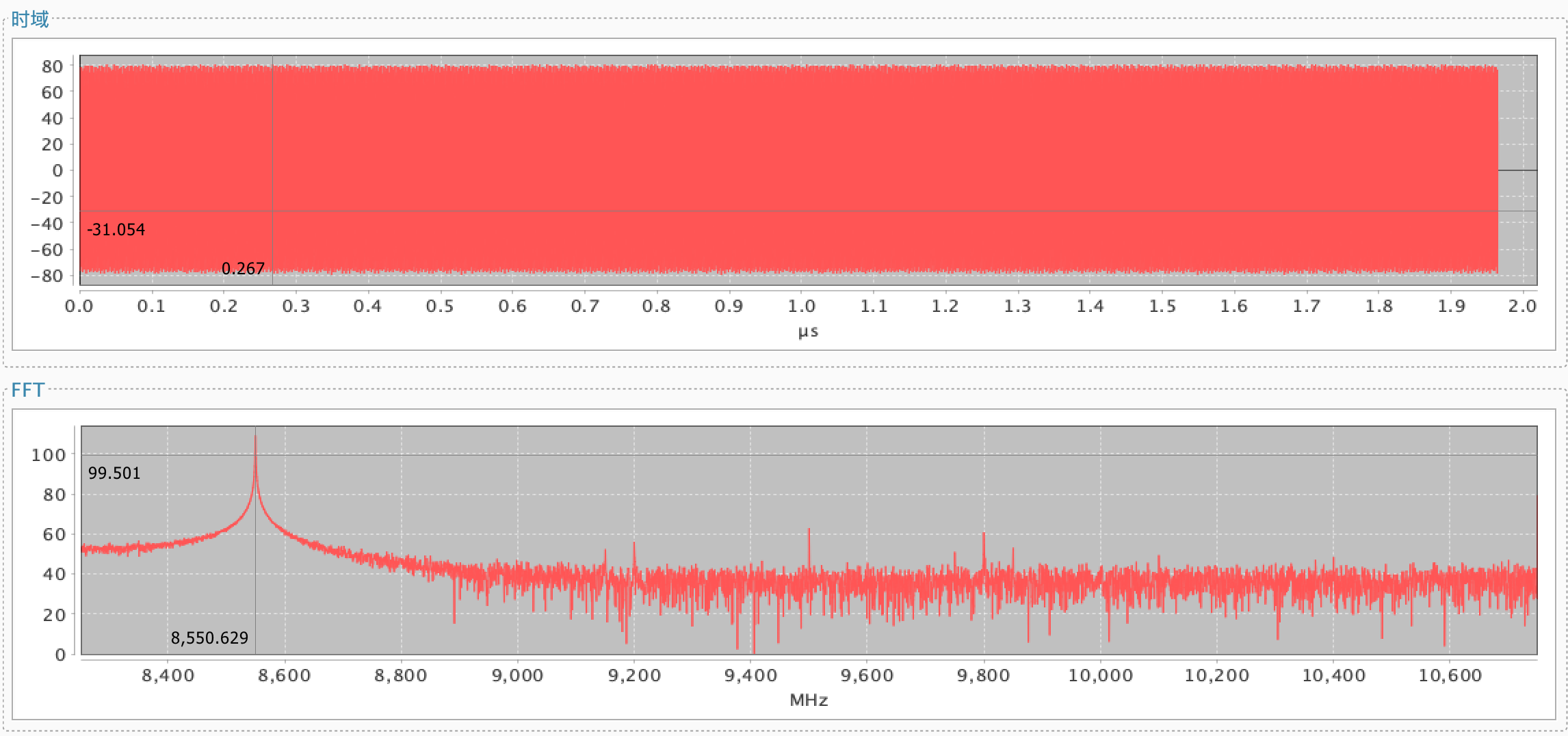
我也不是通信专业的,不懂什么FFT变换,在专业老师的指导下,网上找了相关的算法的代码(如果没有方向,而且专业性特强,很难找),故分享到这里,供有需要的朋友参考。
我一共找到了2个FFT算法,第一个客户说不太对,后来又找到一个,客户说可以了,这边都分享下,供参考选择。
- 第一套
Java文件 Complex.java/** * @description 代表一个复数 */ public class Complex { private final double re; // the real part 实部 private final double im; // the imaginary part 虚部 // create a new object with the given real and imaginary parts 传入实部和虚部,组成一个复数的构造函数 public Complex(double real, double imag) { re = real; im = imag; } // return a string representation of the invoking Complex object @Override public String toString() { if (im == 0) return re + ""; if (re == 0) return im + "i"; if (im < 0) return re + " - " + (-im) + "i"; return re + " + " + im + "i"; } // return abs/modulus/magnitude and angle/phase/argument public double abs() { return Math.hypot(re, im); } // Math.sqrt(re*re + im*im) public double phase() { return Math.atan2(im, re); } // between -pi and pi // return a new Complex object whose value is (this + b) public Complex plus(Complex b) { Complex a = this; // invoking object double real = a.re + b.re; double imag = a.im + b.im; return new Complex(real, imag); } // return a new Complex object whose value is (this - b) public Complex minus(Complex b) { Complex a = this; double real = a.re - b.re; double imag = a.im - b.im; return new Complex(real, imag); } // return a new Complex object whose value is (this * b) public Complex times(Complex b) { Complex a = this; double real = a.re * b.re - a.im * b.im; double imag = a.re * b.im + a.im * b.re; return new Complex(real, imag); } // scalar multiplication // return a new object whose value is (this * alpha) public Complex times(double alpha) { return new Complex(alpha * re, alpha * im); } // return a new Complex object whose value is the conjugate of this public Complex conjugate() { return new Complex(re, -im); } // return a new Complex object whose value is the reciprocal of this public Complex reciprocal() { double scale = re*re + im*im; return new Complex(re / scale, -im / scale); } // return the real or imaginary part public double re() { return re; } public double im() { return im; } // return a / b public Complex divides(Complex b) { Complex a = this; return a.times(b.reciprocal()); } // return a new Complex object whose value is the complex exponential of this public Complex exp() { return new Complex(Math.exp(re) * Math.cos(im), Math.exp(re) * Math.sin(im)); } // return a new Complex object whose value is the complex sine of this public Complex sin() { return new Complex(Math.sin(re) * Math.cosh(im), Math.cos(re) * Math.sinh(im)); } // return a new Complex object whose value is the complex cosine of this public Complex cos() { return new Complex(Math.cos(re) * Math.cosh(im), -Math.sin(re) * Math.sinh(im)); } // return a new Complex object whose value is the complex tangent of this public Complex tan() { return sin().divides(cos()); } // a static version of plus public static Complex plus(Complex a, Complex b) { double real = a.re + b.re; double imag = a.im + b.im; Complex sum = new Complex(real, imag); return sum; } // sample client for testing public static void main(String[] args) { Complex a = new Complex(5.0, 6.0); Complex b = new Complex(-3.0, 4.0); System.out.println("a = " + a); System.out.println("b = " + b); System.out.println("Re(a) = " + a.re()); System.out.println("Im(a) = " + a.im()); System.out.println("b + a = " + b.plus(a)); System.out.println("a - b = " + a.minus(b)); System.out.println("a * b = " + a.times(b)); System.out.println("b * a = " + b.times(a)); System.out.println("a / b = " + a.divides(b)); System.out.println("(a / b) * b = " + a.divides(b).times(b)); System.out.println("conj(a) = " + a.conjugate()); System.out.println("|a| = " + a.abs()); System.out.println("tan(a) = " + a.tan()); } }Java文件:FFT.java, FTT变换的测试在main方法里public class FFT { // compute the FFT of x[], assuming its length is a power of 2 public static Complex[] fft(Complex[] x) { int N = x.length; // base case if (N == 1) return new Complex[] { x[0] }; // radix 2 Cooley-Tukey FFT if (N % 2 != 0) { throw new RuntimeException("N is not a power of 2"); } // fft of even terms Complex[] even = new Complex[N/2]; for (int k = 0; k < N/2; k++) { even[k] = x[2*k]; } Complex[] q = fft(even); // fft of odd terms Complex[] odd = even; // reuse the array for (int k = 0; k < N/2; k++) { odd[k] = x[2*k + 1]; } Complex[] r = fft(odd); // combine Complex[] y = new Complex[N]; for (int k = 0; k < N/2; k++) { double kth = -2 * k * Math.PI / N; Complex wk = new Complex(Math.cos(kth), Math.sin(kth)); y[k] = q[k].plus(wk.times(r[k])); y[k + N/2] = q[k].minus(wk.times(r[k])); } return y; } // compute the inverse FFT of x[], assuming its length is a power of 2 public static Complex[] ifft(Complex[] x) { int N = x.length; Complex[] y = new Complex[N]; // take conjugate for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { y[i] = x[i].conjugate(); } // compute forward FFT y = fft(y); // take conjugate again for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { y[i] = y[i].conjugate(); } // divide by N for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { y[i] = y[i].times(1.0 / N); } return y; } // compute the circular convolution of x and y public static Complex[] cconvolve(Complex[] x, Complex[] y) { // should probably pad x and y with 0s so that they have same length // and are powers of 2 if (x.length != y.length) { throw new RuntimeException("Dimensions don't agree"); } int N = x.length; // compute FFT of each sequence Complex[] a = fft(x); Complex[] b = fft(y); // point-wise multiply Complex[] c = new Complex[N]; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { c[i] = a[i].times(b[i]); } // compute inverse FFT return ifft(c); } // compute the linear convolution of x and y public static Complex[] convolve(Complex[] x, Complex[] y) { Complex ZERO = new Complex(0, 0); Complex[] a = new Complex[2*x.length]; for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) a[i] = x[i]; for (int i = x.length; i < 2*x.length; i++) a[i] = ZERO; Complex[] b = new Complex[2*y.length]; for (int i = 0; i < y.length; i++) b[i] = y[i]; for (int i = y.length; i < 2*y.length; i++) b[i] = ZERO; return cconvolve(a, b); } // display an array of Complex numbers to standard output public static void show(Complex[] x, String title) { System.out.println(title); System.out.println("-------------------"); for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) { System.out.println(x[i]); } System.out.println(); } /*************************************************************************** * Test client and sample execution * * % java FFT 4 * x * ------------------- * -0.03480425839330703 * 0.07910192950176387 * 0.7233322451735928 * 0.1659819820667019 * * y = fft(x) * ------------------- * 0.9336118983487516 * -0.7581365035668999 + 0.08688005256493803i * 0.44344407521182005 * -0.7581365035668999 - 0.08688005256493803i * * z = ifft(y) * ------------------- * -0.03480425839330703 * 0.07910192950176387 + 2.6599344570851287E-18i * 0.7233322451735928 * 0.1659819820667019 - 2.6599344570851287E-18i * * c = cconvolve(x, x) * ------------------- * 0.5506798633981853 * 0.23461407150576394 - 4.033186818023279E-18i * -0.016542951108772352 * 0.10288019294318276 + 4.033186818023279E-18i * * d = convolve(x, x) * ------------------- * 0.001211336402308083 - 3.122502256758253E-17i * -0.005506167987577068 - 5.058885073636224E-17i * -0.044092969479563274 + 2.1934338938072244E-18i * 0.10288019294318276 - 3.6147323062478115E-17i * 0.5494685269958772 + 3.122502256758253E-17i * 0.240120239493341 + 4.655566391833896E-17i * 0.02755001837079092 - 2.1934338938072244E-18i * 4.01805098805014E-17i * ***************************************************************************/ public static void main(String[] args) { int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); Complex x[] = new Complex[N]; // original data for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { x[i] = new Complex(i, 0); x[i] = new Complex(-2*Math.random() + 1, 0); } show(x, "x"); // FFT of original data Complex[] y = fft(x); show(y, "y = fft(x)"); // take inverse FFT Complex[] z = ifft(y); show(z, "z = ifft(y)"); // circular convolution of x with itself Complex[] c = cconvolve(x, x); show(c, "c = cconvolve(x, x)"); // linear convolution of x with itself Complex[] d = convolve(x, x); show(d, "d = convolve(x, x)"); } } - 上面那套,客户看了生成的图后,感觉说不对,所以又找了一套
新建DFT.java/* * Free FFT and convolution (Java) * * Copyright (c) 2017 Project Nayuki. (MIT License) * https://www.nayuki.io/page/free-small-fft-in-multiple-languages * * Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of * this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in * the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to * use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of * the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, * subject to the following conditions: * - The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in * all copies or substantial portions of the Software. * - The Software is provided "as is", without warranty of any kind, express or * implied, including but not limited to the warranties of merchantability, * fitness for a particular purpose and noninfringement. In no event shall the * authors or copyright holders be liable for any claim, damages or other * liability, whether in an action of contract, tort or otherwise, arising from, * out of or in connection with the Software or the use or other dealings in the * Software. */ /** * Downloaded from: https://www.nayuki.io/res/free-small-fft-in-multiple-languages/Fft.java */ public class DFT { /* * Computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of the given complex vector, storing the result back into the vector. * The vector can have any length. This is a wrapper function. * */ public static void transform(double[] real, double[] imag) { int n = real.length; if (n != imag.length) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mismatched lengths"); if (n == 0) return; else if ((n & (n - 1)) == 0) // Is power of 2 transformRadix2(real, imag); else // More complicated algorithm for arbitrary sizes transformBluestein(real, imag); } /* * Computes the inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT) of the given complex vector, storing the result back into the vector. * The vector can have any length. This is a wrapper function. This transform does not perform scaling, so the inverse is not a true inverse. */ public static void inverseTransform(double[] real, double[] imag) { transform(imag, real); } /* * Computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of the given complex vector, storing the result back into the vector. * The vector's length must be a power of 2. Uses the Cooley-Tukey decimation-in-time radix-2 algorithm. */ public static void transformRadix2(double[] real, double[] imag) { // Length variables int n = real.length; if (n != imag.length) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mismatched lengths"); int levels = 31 - Integer.numberOfLeadingZeros(n); // Equal to floor(log2(n)) if (1 << levels != n) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Length is not a power of 2"); // Trigonometric tables double[] cosTable = new double[n / 2]; double[] sinTable = new double[n / 2]; for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) { cosTable[i] = Math.cos(2 * Math.PI * i / n); sinTable[i] = Math.sin(2 * Math.PI * i / n); } // Bit-reversed addressing permutation for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int j = Integer.reverse(i) >>> (32 - levels); if (j > i) { double temp = real[i]; real[i] = real[j]; real[j] = temp; temp = imag[i]; imag[i] = imag[j]; imag[j] = temp; } } // Cooley-Tukey decimation-in-time radix-2 FFT for (int size = 2; size <= n; size *= 2) { int halfsize = size / 2; int tablestep = n / size; for (int i = 0; i < n; i += size) { for (int j = i, k = 0; j < i + halfsize; j++, k += tablestep) { int l = j + halfsize; double tpre = real[l] * cosTable[k] + imag[l] * sinTable[k]; double tpim = -real[l] * sinTable[k] + imag[l] * cosTable[k]; real[l] = real[j] - tpre; imag[l] = imag[j] - tpim; real[j] += tpre; imag[j] += tpim; } } if (size == n) // Prevent overflow in 'size *= 2' break; } } /* * Computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of the given complex vector, storing the result back into the vector. * The vector can have any length. This requires the convolution function, which in turn requires the radix-2 FFT function. * Uses Bluestein's chirp z-transform algorithm. */ public static void transformBluestein(double[] real, double[] imag) { // Find a power-of-2 convolution length m such that m >= n * 2 + 1 int n = real.length; if (n != imag.length) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mismatched lengths"); if (n >= 0x20000000) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Array too large"); int m = Integer.highestOneBit(n) * 4; // Trignometric tables double[] cosTable = new double[n]; double[] sinTable = new double[n]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { int j = (int) ((long) i * i % (n * 2)); // This is more accurate than j = i * i cosTable[i] = Math.cos(Math.PI * j / n); sinTable[i] = Math.sin(Math.PI * j / n); } // Temporary vectors and preprocessing double[] areal = new double[m]; double[] aimag = new double[m]; for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { areal[i] = real[i] * cosTable[i] + imag[i] * sinTable[i]; aimag[i] = -real[i] * sinTable[i] + imag[i] * cosTable[i]; } double[] breal = new double[m]; double[] bimag = new double[m]; breal[0] = cosTable[0]; bimag[0] = sinTable[0]; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { breal[i] = breal[m - i] = cosTable[i]; bimag[i] = bimag[m - i] = sinTable[i]; } // Convolution double[] creal = new double[m]; double[] cimag = new double[m]; convolve(areal, aimag, breal, bimag, creal, cimag); // Postprocessing for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { real[i] = creal[i] * cosTable[i] + cimag[i] * sinTable[i]; imag[i] = -creal[i] * sinTable[i] + cimag[i] * cosTable[i]; } } /* * Computes the circular convolution of the given real vectors. Each vector's length must be the same. */ public static void convolve(double[] x, double[] y, double[] out) { int n = x.length; if (n != y.length || n != out.length) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mismatched lengths"); convolve(x, new double[n], y, new double[n], out, new double[n]); } /* * Computes the circular convolution of the given complex vectors. Each vector's length must be the same. */ public static void convolve(double[] xreal, double[] ximag, double[] yreal, double[] yimag, double[] outreal, double[] outimag) { int n = xreal.length; if (n != ximag.length || n != yreal.length || n != yimag.length || n != outreal.length || n != outimag.length) throw new IllegalArgumentException("Mismatched lengths"); xreal = xreal.clone(); ximag = ximag.clone(); yreal = yreal.clone(); yimag = yimag.clone(); transform(xreal, ximag); transform(yreal, yimag); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { double temp = xreal[i] * yreal[i] - ximag[i] * yimag[i]; ximag[i] = ximag[i] * yreal[i] + xreal[i] * yimag[i]; xreal[i] = temp; } inverseTransform(xreal, ximag); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { // Scaling (because this FFT implementation omits it) outreal[i] = xreal[i] / n; outimag[i] = ximag[i] / n; } } }调用举例
private void drawFFTChart() { //用FFT.java做好像有问题,现在用DFT.java做 // int n = findN(); // Complex source[] = new Complex[n]; // log.info("fft sample num: " + n + ", source sample num: " + ifData.length); int ifDataLength = ifData.length; double[] real = new double[ifDataLength]; // 实部 double[] imag = new double[ifDataLength]; // 虚部 for (int i = 0; i < ifDataLength; i++) { real[i] = ifData[i]; } DFT.transform(real, imag); int fftLength = ifDataLength / 2; double[] fftData = new double[fftLength]; for (int i = 0; i < fftLength; i++) { double abs = Math.hypot(real[i], imag[i]); fftData[i] = 20D * Math.log10(abs); } ((IFFFTChartPane) fftChartPanel).updateChartData(fftData); }
文章评论
Cialis Lo Mejor Enacps - Cialis Meilleur Prix Cialis Generique Omwjsy cialis with dapoxetine</a> Selam J. - buy cialis online with a prescription Gtzest Adverse Reations To Amoxicillin